Table of Contents
Attack Summary Details
- Impacted IRONSCALES customer mailboxes: 100
- Impacted IRONSCALES customers: 83
- Security Bypass: Visual Scanners
- Technique: Social Engineering, Malicious Payload
Background
Ransomware attacks have been on the rise throughout 2021, affecting everyone from large enterprises and government organizations to the individual end-user. Many such attacks are executed via a phishing email, taking advantage of an accessible and exploitable endpoint. This attack demonstrates the criminals’ savvy use of social engineering to lay the first step of the trap.
The Attack: Method & Payload
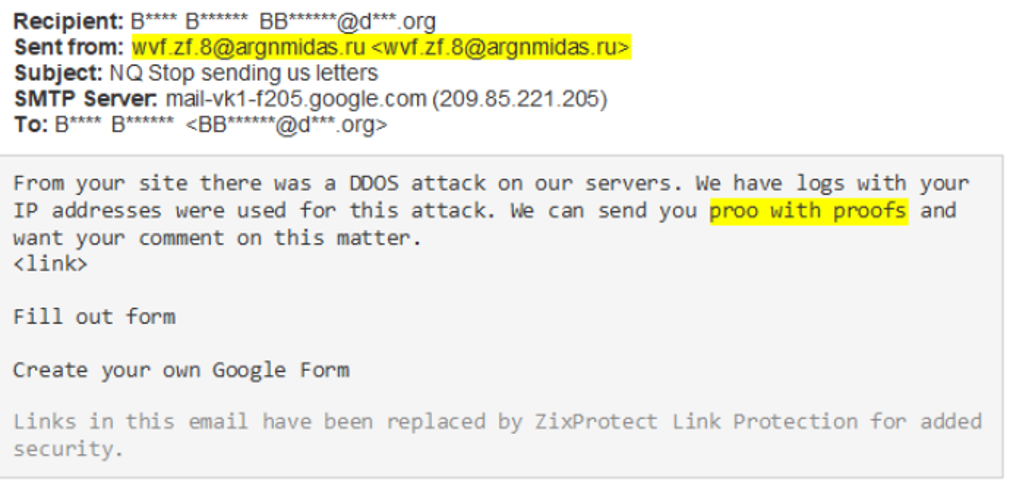
In this attack, the recipient receives an email that claims a DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service attack) was executed via their website on the senders’ servers. The attacker indicates that they can provide proof of such if some action is taken. In the first phase of this attack, the “action” is to engage a link that will execute a script that initiates the ransomware malware. In the second phase of the attack, the “action” is to reply to the email which will set up the malware stage of the attack.
Phase 1
Phase 2
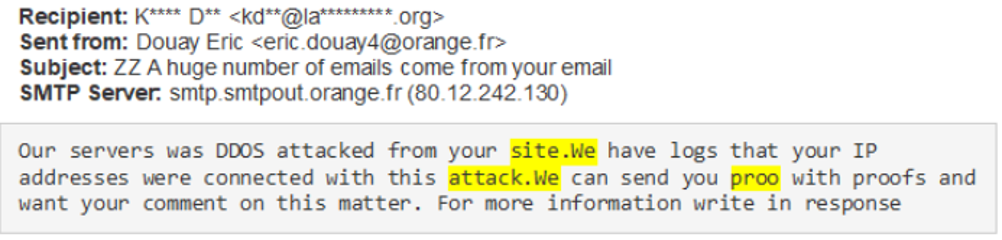
Payload
The payload in this attack is a malicious script that is hosted in one of Google’s development platforms: Google APP Scripts. Cybercriminals frequently use this service to host malicious software or links as the domain has a good reputation and thus bypasses scanners and other detection mechanisms.
What to Look For
From the perspective of the end-user at the mailbox level, there are some anomalies that can provide clues that this is a phishing threat. The phase 1 email contains an email address in the sender name field. While this can be legitimate in some cases, it is abnormal in a personal email such as this and should raise some questions. Additionally, the spelling mistakes highlighted in the examples above are frequent amongst phishing emails. Lastly, the links from “script.google.com/macros” should always be treated with care and should not be opened unless they are expected, and intentions are known.
How We Spotted the Attack
Our AI, named Themis, was able to spot this attack based on our behavioral and textual anomaly detection capabilities. Once our platform identified this as a phishing attack, we immediately pulled the emails out of the inboxes of all our impacted customers.
To learn more about IRONSCALES’ fully integrated anti-phishing and security and awareness training solution, please sign up for a demo today at https://ironscales.com/get-a-demo/.
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)








.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)





