Guide to Phishing Prevention Best Practices
According to an Osterman Research report, phishing has worsened for most organizations. With the increasing sophistication of cybercrime gangs and the complexity of modern IT infrastructure, this should be no surprise. Fortunately, an entire anti-phishing ecosystem has developed to arm security engineers and IT administrators with tools for combatting the onslaught of phishing threats.
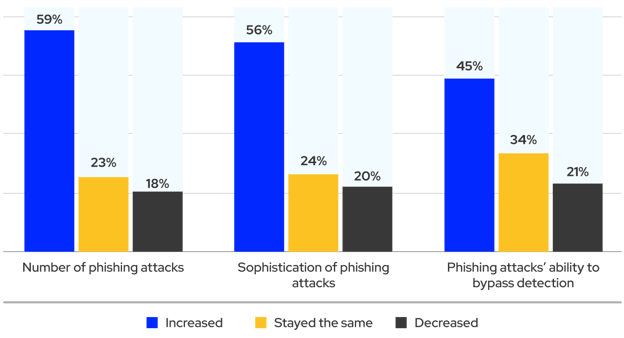
80% of organizations report that phishing has worsened or remained the same. (Source).
This article will introduce six essential phishing prevention best practices that enable organizations to limit the risk of a phishing attack impacting them. In addition to the traditional mitigations, we’ll cover tools like SEGs (secure email gateways) and cutting-edge email security technologies like Integrated Cloud Email Security (ICES) solutions.
Summary of key phishing prevention best practices
The table below briefly summarizes the six phishing prevention best practices we will explore in this article. We’ll expand on these topics to make integrating these practices into your organization’s security ecosystem easier.
| Best Practice |
Description |
|
Implement email security best practices
|
Email can be protected from general threats (including phishing but also much more). For example, Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace include advanced phishing protection functionality and user authentication managers to reduce the threat of credential breaches and account takeovers.
|
| Leverage AI and machine learning |
Add technology to your stack that uses AI and machine learning models that learn what is normal user behavior for each inbox to detect anomalous behavior that human analysts and traditional gateways tend to miss. |
| Embrace crowdsourcing intelligence |
Your email security architecture should take advantage of intelligence from the members of your organization and other protected organizations. Users are empowered to share insights about zero-day and emerging phishing attacks across different organizations. |
| Integrate and orchestrate security events and response |
SIEM and SOAR are powerful security technologies that amplify your ability to monitor and quickly respond to threats; ensure your email security solutions are integrated with these centralized security tools. |
| Conduct employee security awareness training (SAT) |
Your employees can be an excellent source of intelligence, especially for zero-day attacks, but to leverage them optimally, you should regularly train them to identify and report potential threats. |
| Use phishing simulation testing |
Test the susceptibility of an organization's employees to phishing attacks by regularly sending them mock phishing emails. Look for solutions that can track and report engagement and results so you know who needs additional training and how your organization would perform in the event of an actual attack. |
Six essential phishing prevention and protection best practices
The best practices outlined above may seem like a few simple changes, and for organizations with a mature security posture, they may be simple to adopt. However, if an organization starts from scratch or has an immature email security stack, the practices above may require multiple complex changes and technologies. Therefore, organizations with a less mature security posture will likely benefit from a holistic platform that automates as much of this work as possible.
Whether you implement these practices manually or leverage a fully-featured anti-phishing platform, you’ll want to understand each practice and why it matters. We’ll review each phishing prevention best practice individually in the sections below.
Implement email security best practices
When it comes to email security, the first technology that will come to mind is DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance). This protocol builds on SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) to make it harder for attackers to impersonate your domain when sending phishing emails to others. Thus, you can configure your SEG or email platform to reject or fail incoming mail that fails authentication checks However, DMARC, SPF, and DKIM are just the tip of the iceberg.
There are also solutions built into specific email platforms. For example, Google Workspace offers the Advanced Protection Program, and Microsoft 365 offers Microsoft Defender for Office 365. These platforms provide several email security features. For example, you can mark external domains to make identifying phishing attempts that use similar-looking domain names easier.
Regardless of your email platform, the traditional anti-phishing practice is to deploy a secure email gateway (SEG). SEGs scan incoming and outgoing emails for various types of malicious content, such as viruses, spam, phishing emails, and other malware. Nowadays, many security managers are swapping older SEG solutions for a more modern Integrated Cloud Email Security (ICES) solution. ICES (Integrated Cloud Email Security).
ICES solutions are cloud-native anti-phishing solutions that use APIs to integrate with cloud email platforms like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365. Unlike SEGs, an ICES doesn’t require you to change your MX record; they also go beyond SEGs by providing prompts for users to help reinforce training and detect compromised accounts.

Leverage AI and machine learning
AI/ML (artificial intelligence and machine learning) continues to undergo stunning breakthroughs. You can take advantage of these innovations to defend your organization against phishing. Intelligent algorithms based on huge datasets can search for patterns that are effectively invisible to the best human analysts.
Major platforms already use machine learning algorithms to separate suspicious mail based on complex patterns. However, there are also external services dedicated to leveraging AI/ML models to detect phishing threats. Such services can use cutting-edge developments to identify threats and activate the appropriate playbook in your SOAR. However, not all AI/ML solutions are equal. Many are based on stale data or receive new data too slowly. It’s also possible for models to train on data that simply isn’t very relevant.
IRONSCALES uses an approach that combines AI and human insights. The technology integrates with cloud-based email services like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace using APIs. The platform employs AI modules such as natural language understanding (NLU) and natural language processing (NLP) to establish normal inbox behavior and identify anomalies.
The AI-powered virtual SOC analyst, "Themis," analyzes email content and detects advanced phishing attacks. Additionally, IRONSCALES leverages feedback from over 20,000 analysts in its global network to continually improve AI and machine learning modules.
You can learn more about the details of anti-phishing AI/ML models from our blog post on Developing a Machine Learning Model to Identify Phishing Emails.
Embrace crowdsourcing intelligence
AI/ML learning models trained exclusively on historical data suffer from a key inadequacy: they are incapable of detecting emerging phishing threats in real time. The solution is to empower users to provide AI/ML models with real-time insights about possible threats.
Doing this within your organization is good, but it’s even better when this intelligence is shared across thousands of companies. For example, IRONSCALES makes it possible to anonymously collaborate with over 20,000 security analysts worldwide by vetting incoming phishing reports from its customers and feeding this data to their AI/ML models.
Integrate and orchestrate security events and response
M-SOAR (email security orchestration, automation, and response) applies the framework and benefits of a SOAR to the particular needs of email security. The basic idea is to introduce modern security automation infrastructure to prevent phishing. Using email security automation, M-SOAR decouples MTTR (mean time to recovery or mean time to restore) from human response time.
Many SOAR solutions (and the sources that feed them, like SIEMs) have improved their interoperability with email security vendors. Commercial solutions specializing in phishing protection and email security should also offer API integrations for coordinating with your existing SOAR architecture.

Conduct employee security awareness training
Basic security practices like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong passwords are a great first line of phishing protection defense. However, employee security awareness training (SAT) goes beyond simply teaching employees to adhere to basic security best practices. SAT is also about teaching employees to recognize phishing emails, business email compromise (BEC) attacks, VIP impersonations, and other threat indicators.
Well-trained employees are less prone to fall for phishing attacks. SAT should be delivered regularly, and organizations should analyze employee engagement with the material to ensure employees understand the concepts. SAT also improves crowdsourced intelligence because employees with security awareness are better able to detect potential threats.
You can learn more about implementing Security Awareness Training by checking out our.
Use phishing simulation testing
No single technology or email security stack can stop 100% of all phishing attacks, especially when we consider the threat posed by zero-day and emerging attacks. Therefore, it is important to evaluate the phishing protection provided by your last line of defense: your employees. Only a realistic simulation will let you know how your employees will react during a real attack.
Setting up a phishing simulation can seem daunting at first. Fortunately, solutions simplify and automate the process so that anyone on your team can launch an effective phishing simulation campaign.
How to implement a phishing simulation campaign
To demonstrate this, let’s look at the process of setting up a phishing simulation using the IRONSCALES web interface.
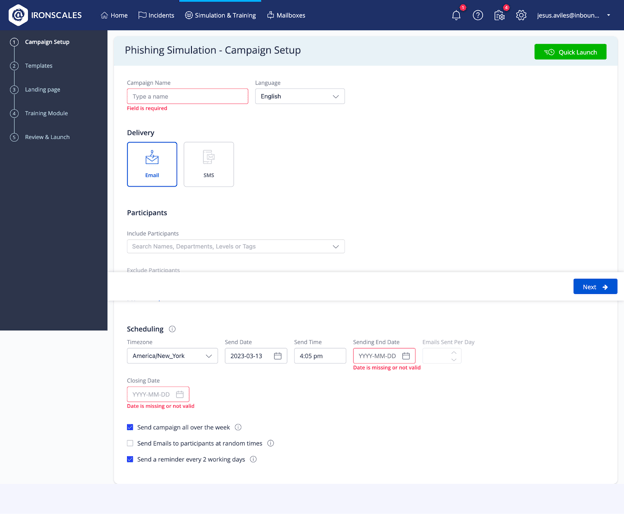
To start, we establish some basics. For this example, we’ll leave the inputs empty and just go through the different configuration screens.
To start, we establish some basics. For this example, we’ll leave the inputs empty and just go through the different configuration screens.
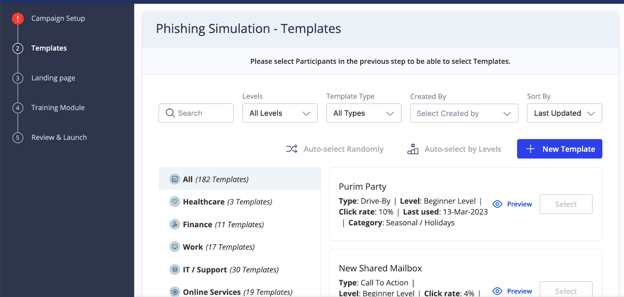
Next, the web app allows us to select a template. These are pre-made messages inspired by real-life phishing examples.
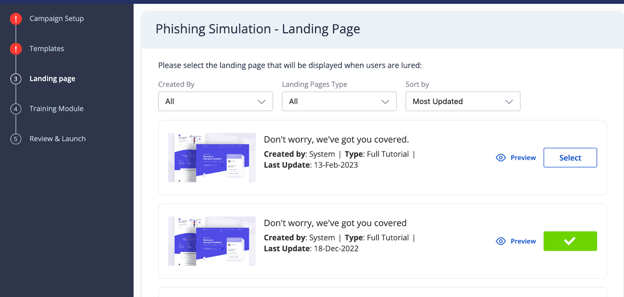
Users that click a phishing link will be taken to a landing page. You can select what this landing page will be using this screen.
Now we arrive at a crucial step: selecting the training module. The training module is the content provided to employees who fall for a phishing simulation. This step is vital because it will enable employees who fail a test to learn how to detect similar attacks in the future.

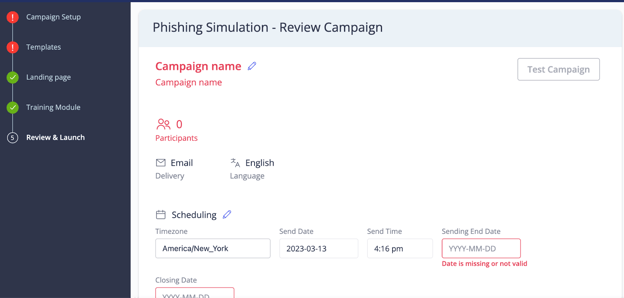
Finally, we can review our chosen settings and launch the phishing campaign.
In this example, we’ve left everything blank, but you’d now be ready to begin the campaign in real life!
Conclusion
Phishing is a growing problem, and although mitigations exist, it’s still immensely challenging to prevent sophisticated social engineering attacks. Luckily, anti-phishing tools are constantly improving. A holistic defense against phishing requires combining classic mitigations (like SEGs, SAT, and phishing simulation testing) with modern ICES solutions that leverage AI/ML and human insights to detect novel threats to your organization.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)















