Table of Contents
Background
UPDATE as of 3/31
IRONSCALES researchers are continuing to monitor the spear-phishing attack impersonating the MacKenzie Bezos Scott foundation.
Since posting this blog, we have seen the scam continue to proliferate, with the total number of mailboxes affected now at 190,000 and over 200 IRONSCALES customers targeted.
Cybercriminals continue to innovate their attack methods. IRONSCALES recently identified a specific attack that affected over 200 of our customers. In this instance, attackers deployed a phishing attack that impersonated a well-known and highly respected philanthropical organization named the Mackenzie Bezos-Scott foundation using what is known as an Advance Fee Scam.
The phish
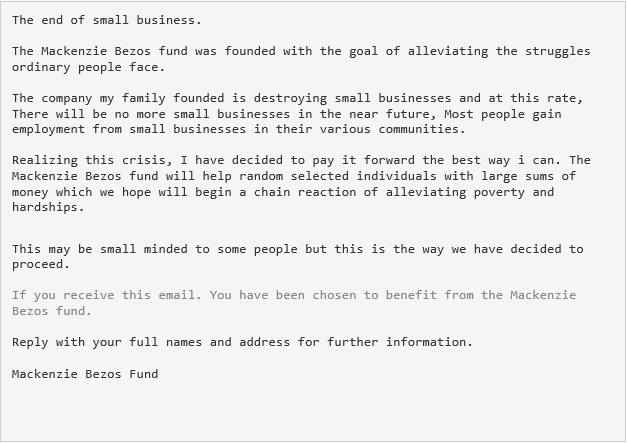
End-users received an email that appeared to be from the MacKenzie Bezos-Scott grant foundation that purports that they had been selected for a grant. To initiate the process to receive the funds, the user was asked to reply to the email with their full name and address. Once the recipient followed through with the request to provide personal details, the attacker asked for a small processing fee in order to initiate the grant payment transfer.
 The warning sign that something is wrong
The warning sign that something is wrong
At first glance the email appears to have been sent from a legitimate address and the content overall made sense. There were no links or attachments in the email, which are common signs of a phishing attack and easily detected. So to the average reader, all might have appeared to be on the up and up. However, upon further inspection the reader should have noticed the differences in the text. Have a look again to see if you can spot the difference (hint: look for changes in the text color.)
The danger here was the end user potentially being duped into replying to the email with their personal and financial details.
Why the attack could work
In this attack, the senders almost certainly used social engineering to identify an exact set of victims who would believe that such an email was legitimate due to their title/position and/or because of the industry they work in. In addition, the attackers no doubt used the fact that many individuals and organizations are struggling financially due to the pandemic and that the foundation (and its high-profile namesake) had been quite vocal in their desire to provide grants totaling over $9 Billion to organizations such as charities, non-profits and small businesses in need.
How we identified the attack
While this attack was sophisticated in its targeting, there were textual and technical anomalies in the body of the email that we were able to identify and quickly determine that this was a phish. Look at the email below and see if you can spot the signs of attack:
- The sender’s name was shown as “Mackenzie Scott Grant”, but the return email address was to the domain @mintme.com. This is a preliminary sign of an impersonation attack.
- There were multiple grammatical errors in the text of the email, including improper punctuation and capitalization. This is a hallmark of phishing emails.
- Finally, there was inconsistency between the sender’s name and the signature block of the email. This is another common trait of a phish
Recipient: D***** D**** <********@*****.com>
Sent from: Mackenzie Scott Grant <no-reply@mintme.com>
Subject: Hello --1
SMTP Server: xtrwsqzp.outbound-mail.sendgrid.net (167.89.100.227)
To: YOU <no-reply@mintme.com>
Upon identifying this attack we immediately flagged and removed all affected emails across all of our 200+ impacted customers before any further damage could be done.
Identifying and remediating advanced phishing threats
This was an example of a clever and targeted phishing attack. Imagine being an overworked, stressed out employee at an organization struggling financially due to the pandemic and seeing this show up in your email. With no obvious warning signs at first glance in the email itself, it could be understandably tempting to respond.
We invite you to learn more about how IRONSCALES can fight against this and many other types of phishing attacks by combining human and machine intelligence. Learn more at www.ironscales.com today.
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)











.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)



