Table of Contents
Email spoofing has evolved. Modern spoofing campaigns leverage trusted SaaS platforms, API abuses, and protocol vulnerabilities to bypass traditional email security filters.
Recent examples include attackers exploiting DocuSign’s Envelopes API to distribute authentic-looking invoices from legitimate domains and leveraging vulnerabilities such as Microsoft's CVE-2025-21259, allowing attackers to forge Outlook email headers.
Organizations need layered defenses backed by AI and human insights to effectively combat these new tactics. Let's talk about how you can reinforce your Outlook environment today.
Five Technical Controls to Stop Spoofing in Outlook
Below are five critical controls to implement immediately in your Outlook environment:
1. Enable Multifactor Authentication (MFA)
Why It Matters
Stolen credentials remain attackers' primary entry vector for Business Email Compromise (BEC). MFA significantly reduces unauthorized access, even when passwords are compromised through advanced social engineering or deepfake-assisted phishing.
What to Do
- Enforce MFA for Outlook and Microsoft 365 accounts using FIDO2 security keys or authenticator apps.
- Apply Conditional Access policies requiring step-up authentication or blocking logins from unknown locations or risky IP addresses.
- Disable legacy authentication protocols (IMAP, POP, SMTP AUTH).
2. Configure SPF and DKIM Records Accurately
Why It Matters
Properly configured SPF and DKIM records authenticate email senders. Misconfigured or incomplete records create vulnerabilities that attackers exploit for spoofing.
What to Do
- Include all legitimate sending services explicitly in your SPF TXT record, limiting DNS lookups to under ten.
- Sign all outbound mail using DKIM with properly maintained keys (selector._domainkey.example.com).
- Revalidate SPF and DKIM records regularly, especially after onboarding new SaaS email services.
3. Implement DMARC Policies
Why It Matters
DMARC provides policy enforcement and visibility on top of SPF and DKIM. Organizations lacking DMARC remain highly vulnerable to email spoofing attacks and delivery disruptions.
What to Do
- Begin with a DMARC policy set to "none" (v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@yourdomain) to monitor and gather reports.
- Transition to "quarantine" and subsequently "reject" policies after validating reporting data over 30 to 45 days.
- Analyze DMARC aggregate and forensic reports to continuously refine sender authentication.
4. Maintain a Rapid Patch Management Process
Why It Matters
Attackers frequently exploit known vulnerabilities in email servers, clients, and security gateways. Rapid patching reduces exposure and limits attacker footholds.
What to Do
- Apply Microsoft "Patch Tuesday" updates within seven days for Outlook, Exchange Server, and Windows environments.
- Subscribe to CVE vulnerability notifications for third-party email security appliances and apply firmware updates promptly.
- Conduct regular vulnerability scans for webmail (OWA), SMTP relays, and email security gateways.
5. Run Continuous Security Awareness Training
Why It Matters
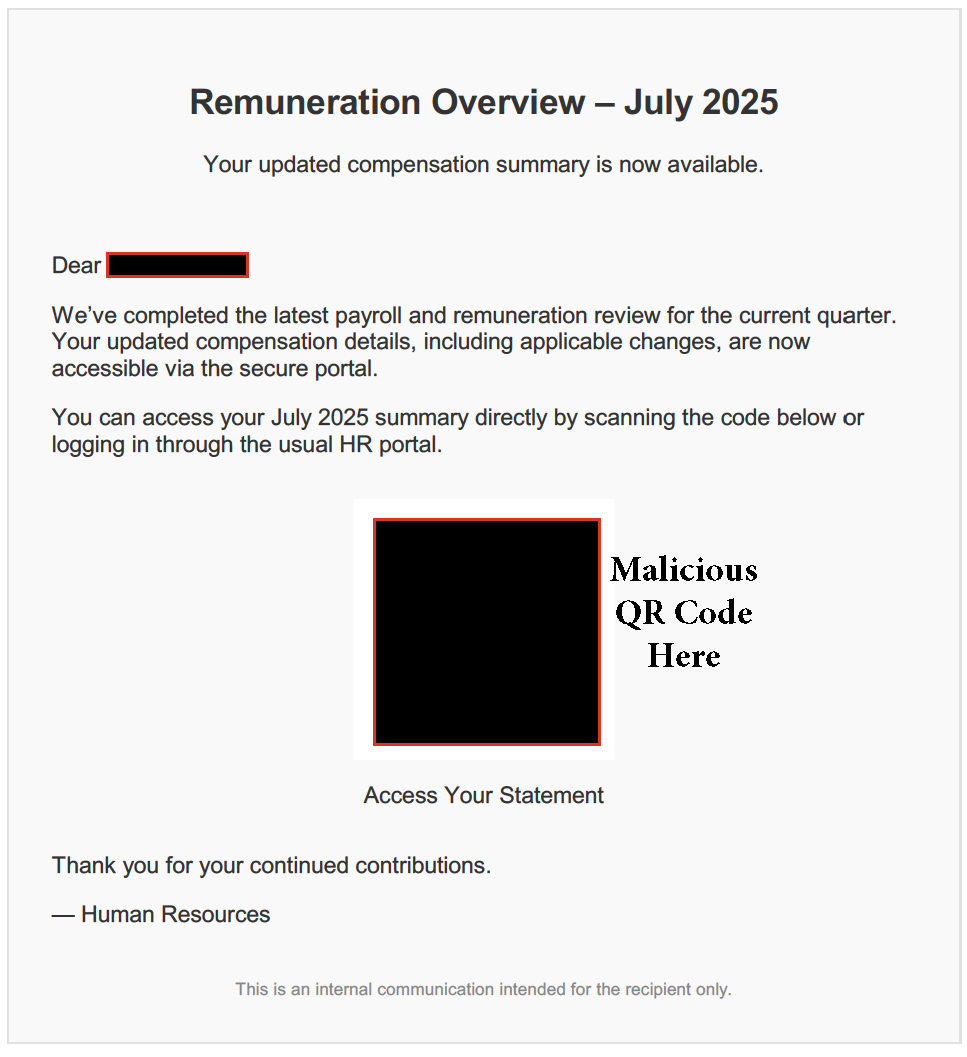
Human users remain a significant target for phishing attacks. Sophisticated phishing now incorporates AI-generated content, deepfake audio, and QR codes ("quishing"). Continuous training effectively reduces user susceptibility.
What to Do
- Execute short, frequent phishing simulation exercises every four to six weeks, providing immediate micro-training based on responses.
- Track key metrics such as phishing click rates, credential submission attempts, and user reporting effectiveness.
- Regularly update training scenarios to reflect emerging threats, including deepfake impersonation, invoice fraud, and QR-code phishing.
Spotting GenAI-Driven Phishing
Use this checklist when reviewing suspicious messages in Outlook:
- Sudden changes in writing style or tone inconsistent with known sender history.
- Overuse of imperative language or complex sentence structures.
- Correct grammar but incorrect or outdated business contexts.
- Invisible Unicode or zero-width characters inserted in URLs or headers.
- Embedded QR codes or unusual attachments like voice notes.
- Discrepancies between display names and authenticated sending domains.
All of these are tell tale signs of GenAI phishing. This brings me to my next point. Manual identification of GenAI phishing has become increasingly difficult due to advancements in modern artificial intelligence platforms utilization for nefarious purposes.
Leveraging AI within your defensive strategy provides the strongest protection.
How IRONSCALES Accelerates These Controls
IRONSCALES integrates Adaptive AI with continuous human feedback to deliver comprehensive inbox-level protection. The platform analyzes sender behaviors, language patterns, and relationship anomalies, automatically detecting and remediating threats. IRONSCALES integrates seamlessly with Microsoft 365 via a simple three-click API setup, requiring no MX record modifications.
Our latest DMARC Management and Monitoring solution automates DMARC record maintenance, simplifies policy enforcement, and provides detailed forensic reporting. This ensures continuous compliance and accurate sender authentication, reducing the complexity traditionally associated with managing DMARC.
Not sure your current defenses are doing the trick? Dealing with phishing threats reaching your end users at an increasingly alarming rate? Reach out to our team today for a complimentary 90-day email security scan back to reveal previously undetected threats.
Learn how IRONSCALES can keep your Outlook users safer than the competition.
We catch the phish others miss.
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)









.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)