Table of Contents
Background
Cybercriminals continue to innovate their attack methods. IRONSCALES recently identified a specific attack that affected over 40 of our customers. In this instance, attackers impersonated a government agency in the State of NY to steal user credentials in seeking to prey on citizens receiving unemployment benefits.
The phish
This attack employed social engineering tactics to coerce the victim to click on a malicious link and enter their credentials. The attackers would harvest these credentials and either use them to attempt to steal funds from the victims or sell the credentials to other criminals looking to do the same. In this attack the threat actor sent an email purporting to be from the Unemployment Agency of the state of New York. The phishing email told the recipient that their unemployment payments have been placed on hold and to retrieve the payments, that they must update their user credentials using the link included in the email.
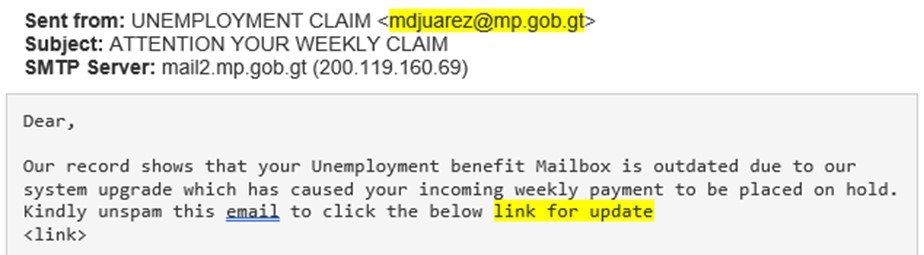 The payload
The payload
The payload is embedded as a link in the email body. If the victim clicked on the link they directed to fake lookalike landing page. From here, the victim would input their credentials, which then be harvested by the attacker for follow-up attacks or future fraud.
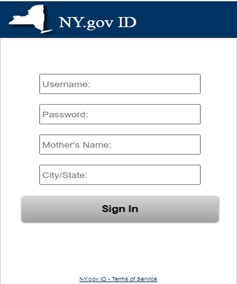
Why the attack could work
In this attack, it is possible that the attackers had used social engineering techniques to identify people who were currently unemployed in the State of New York (this is a simple search on professional platforms like LinkedIn) and use that information to make an informed decision that these same people were currently receiving unemployment benefits. Those recipients who were actually receiving such benefits would not necessarily be alarmed by receiving such a notification. The victims would also not be alarmed by the landing page they were directed to, as they would be familiar with the page from previous online interactions with this agency and would have a difficult time discerning any differences between the authentic page and this fake one. The font, color, credentials fields and even the “Terms of Service” link were similar enough to draw the victim into the attack.
How we identified the attack
We initially detected this attack through our community reporting mechanism when several customers notified us of this attack. Next, Themis’, our AI analyst’s, sender behavior analysis and our AI clustering mechanism assisted in identifying similar attacks with over forty of our customers. This powerful combination of technologies and our Community of customer security teams gave us the ability to stop this attack from the start, while providing IRONSCALES with the ability to predict and prevent future attacks of this variety.
Identifying and remediating advanced phishing threats
This is an example of a clever and targeted phishing attack. Imagine being stressed out by being unemployed and relying on your unemployment benefits to get by until you found another job and then receiving this email. With the panic that would immediately set it and there not being obvious warning signs at first glance in the email itself, it could be understandably tempting to click the malicious link.
This attack bypassed Microsoft O365 integrated protection, SPF and DKIM. These authorization technologies and SEG are good at detecting large scale phishing campaigns coming from suspicious/blocklisted domains and servers. However, they remain weak in their ability to identify more advanced email threats like the one described here.
We invite you to learn more about how IRONSCALES can fight against this and many other types of phishing attacks by combining human and machine intelligence. Learn more at www.ironscales.com today
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)








.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)





.png)