Table of Contents
Computer Vision Explained
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence that focuses on giving machines the ability to interpret, analyze and understand visual data from images or videos. This can include recognizing objects in an image, understanding the context of an image or scene, interpreting facial expressions, tracking motion, and more.
Computer vision algorithms are typically trained using labeled datasets to teach the machine how to interpret and analyze the data. With advancements in machine learning, computer vision is becoming increasingly powerful and can be used in a variety of applications such as autonomous vehicles, facial recognition systems, and healthcare imaging.
How does computer vision work?
Computer vision algorithms use various techniques to process digital images, including edge detection, segmentation, motion estimation, pattern recognition, object detection, and classification. The ultimate goal is for the algorithm to identify specific features or objects within the image, and then make decisions based on what it sees.
Computer vision algorithms can be applied in a number of different ways. For example, they can be used to identify patterns in images or videos, detect faces or objects, track movement, classify images into categories, and recognize handwritten text.
How does computer vision improve threat protection?
Computer vision can be used to detect threats in a variety of ways, from identifying suspicious objects and behavior in images and videos to recognizing known malicious activities. Computer vision can also be used for facial recognition to help identify potential criminals or individuals with suspect intentions.
By using computer vision algorithms, security systems are able to analyze patterns and behaviors that may indicate a potential threat and alert authorities in real time. Additionally, computer vision can be utilized to detect anomalies in data sets that could indicate malicious behavior or cyberattacks. By using powerful image processing techniques such as object detection, classification, segmentation, tracking, and pattern recognition, computers are able to better identify potential threats and help protect against them.
In the case of phishing attacks, computer vision can be used to detect fake login pages used for credential harvesting. Computer vision uses image processing techniques to check for inconsistencies in web page designs. It can also scan through various text and images on the website to ensure that all the elements belong to legitimate websites and not those created by criminals. By using computer vision for these purposes, businesses can be better protected from potential malicious activities.
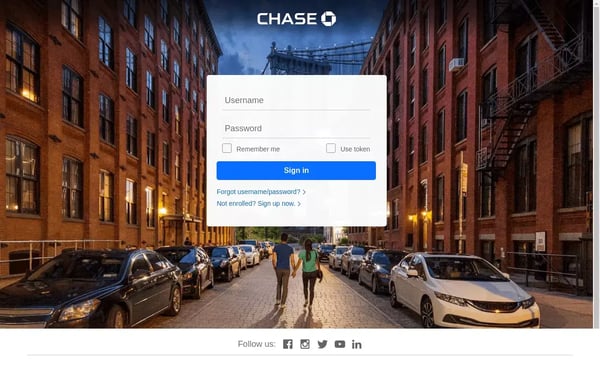
How IRONSCALES ™ Uses AI-Based Computer Vision to Prevent Credential Theft Attacks
IRONSCALES has the ability to identify fake login pages using AI, computer vision, deep learning, and NLU technology built into its self-learning email security platform. Computer Vision and Natural Language Understanding (NLU) empower the IRONSCALES solutions to automatically baseline human behavior and normal activity.
This enables the platform to understand both the content and intent (“what”) of suspicious messages, and at the same time, validate sender identity and domain authenticity (“who”), which is what legacy email security tools and authentication protocols focus on. This added contextual analysis not only helps to identify social engineering, but it enables verdicts to be rendered before an email hits an employee’s inbox. Learn more about the how IRONSCALES uses computer vision and natural language understanding to identify social engineering in our blog post.
Computer vision and AI also play a role in detecting fake login pages, and identifying visual anomalies based on learned and trusted profiles (legitimate login pages/websites). While there are some indicators of compromise with fake login pages, such as blurred images, retro branding, and a suspicious sense of urgency, many are unidentifiable using legacy anti-phishing technology or the naked eye. Further, our NLU uses advanced machine learning (ML) and neural networks to identify the ‘what’ is being sent by analyzing fraudulent language. This allows us to render a verdict on the legitimacy of business email compromise messages, particularly the ones being deployed for credential theft, in real time. You can learn more on computer vision in the IRONSCALES platform helping prevent credential harvesting in our blog post.
Get a demo of IRONSCALES™ today! https://ironscales.com/get-a-demo/
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)