Table of Contents
Malicious cyber activity goes far beyond email security, with some estimates putting the cost to the U.S. economy between $57 billion and $109 billion in 2016 alone. The potential impact on the global economy is staggering, with recent estimates placing the annual cost at $10.5 trillion by 2025.
For the U.S. government, and the Department of Defense (DoD) in particular, the greatest threat is to the integrity of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). CUI is defined as “information the Government creates or possesses, or that an entity creates or possesses for, or on behalf of, the Government, that a law, regulation, or Government-wide policy requires or permits an agency to handle using safeguarding or dissemination controls.”
The continued loss of CUI from the Defense Industrial Base (DIB) sector represents a monumental risk to national security. In an effort to reduce this risk, the DoD has established the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC).
Measuring cybersecurity maturity
A unifying standard for implementing cybersecurity measures across Department of Defense (DoD) contractors, the CMMC comprises five distinct “maturity” levels, each with associated processes and 171 cybersecurity best practices. Any company within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB) – regardless of size, business model, or location – will need to meet CMMC requirements to bid on DoD contracts.
At present, there are more than 300,000 companies in the DIB supply chain. Meeting the standard will compel each of these companies to verify that the processes and practices associated with each maturity level have been successfully implemented. The interim rule implementing CMMC became effective on November 30, 2020 but must complete a congressional review before it becomes permanent.
Validating readiness across the supply chain
The CMMC is the DoD’s response to the unchecked compromise of sensitive information housed on contractors' information systems. It provides assurances on multiple levels.
Officially, the DoD is migrating to the new CMMC framework “in order to assess and enhance the cybersecurity posture of the Defense Industrial Base (DIB) sector. The CMMC is intended to serve as a verification mechanism to ensure that DIB companies implement appropriate cybersecurity practices and processes to protect Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) within their unclassified networks.”[1]
Put more simply, companies that have met the CMMC standard have proven they can adequately protect sensitive unclassified information, both within their own organization, and throughout a multi-tiered supply chain.
Understanding the five levels of certification
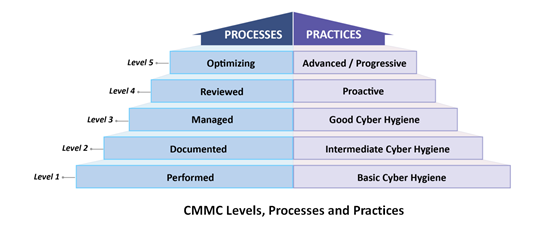
Five Levels of Certification
The CMMC’s five certification levels indicate the maturity of a company's cybersecurity infrastructure, particularly its ability to safeguard sensitive government information. The five levels are tiered and cumulative, so each successive level builds upon the technical requirements of those beneath it, with its own set of processes and practices. The processes range from “performed” to “optimizing,” and the practices from “basic cyber hygiene” to “advanced/progressive.”
|
Level 1 |
Goal: Safeguard Federal Contract Information (FCI) Processes: Performed Practices: Basic cyber hygiene |
|
Level 2 |
Goal: Serve as transition step in cybersecurity maturity progression to protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) Processes: Documented Practices: Intermediate cyber hygiene |
|
Level 3 |
Goal: Protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) Processes: Managed Practices: Good cyber hygiene |
|
Level 4 |
Goal: Protect CUI and reduce risk of advanced persistent threats (APTs) Processes: Reviewed Practices: Proactive |
|
Level 5 |
Goal: Protect CUI and reduce risk of advanced persistent threats (APTs) Processes: Optimizing Practices: Advanced/progressive |
Becoming certified
The independent CMMC Accreditation Body (CMMC-AB) will authorize and accredit CMMC Third Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAOs) and the CMMC Assessors and Instructors Certification Organization (CAICO) in accordance with DoD requirements.
To become certified, a DIB company must select an authorized and accredited C3PAO from the CMMC-AB Marketplace website. The C3PAO will assess the company’s unclassified networks and, based on the results, issue appropriate CMMC certificates.
Taking the next step
DoD contractors should begin preparing for certification by learning the CMMC's technical requirements, with an eye on long-term cybersecurity strength. We strongly encourage contractors to review existing processes and identify any that meet CMMC standards, together with developing a plan to implement and adopt any other practices to obtain the highest possible certification level. Those that do will be well positioned to bid on new contracts when the rule becomes permanent.
To learn more about CMMC, visit the CMMC website, which includes assessment guides, timeframes for implementation, and a helpful FAQ.
To learn more about IRONSCALES’ award-winning anti-phishing solution, please visit us today at.
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)









.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)





.png)