Table of Contents
IRONSCALES researchers have identified a trending fake login attack spoofing two leading email delivery service providers, Mailgun and SendGrid. This phishing attack was discovered just weeks after our researchers disclosed a massive phishing attack targeting PBX voicemail integrations.
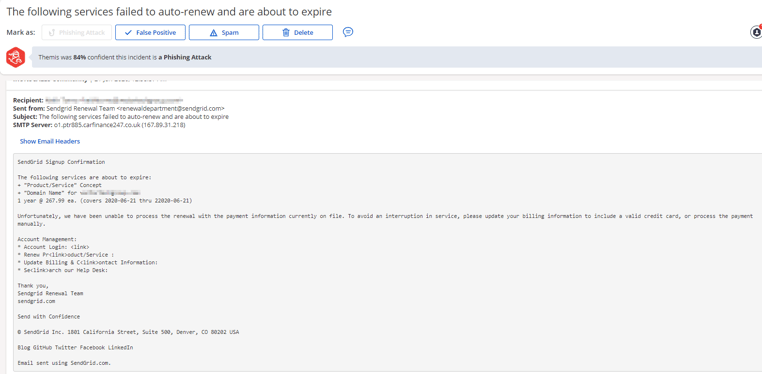
The attacks spoofing Mailgun and SendGrid (see figures 1-4 below), which were first discovered in early June, attempt to trick recipients into believing that “the following services failed to auto renew and are about to expire.” Such spoofing messages, which appear to come from “renewal teams,” provide a link to a fake phishing website where recipients are prompted to “update” their credit card on file so as to avoid any disruption in service.
With close to 100,000 customers worldwide between Mailgun and SendGrid, it’s no surprise that attackers would setup a fake login attack campaign targeting customers (and likely those that aren’t customers but could be susceptible to social engineering).
So far, IRONSCALES has used computer vision to identify the attack as potentially having bypassed secure email gateways and DMARC in over 5,000 mailboxes in more than 200 companies across the US, Canada and Europe. The attack initially appeared to focus on companies within the travel and hospitality industries, which makes sense when considering how reliant companies within these industries are on email marketing.
Additionally, however, we have also found recent examples of this attack targeting the legal, healthcare, financial services and manufacturing industries, suggesting that the attackers have automated this campaign to reach the broadest audience possible. IRONSCALES is now currently exploring whether or not other email delivery service providers are also under attack.
Figures 1 + 2 [Mailgun]

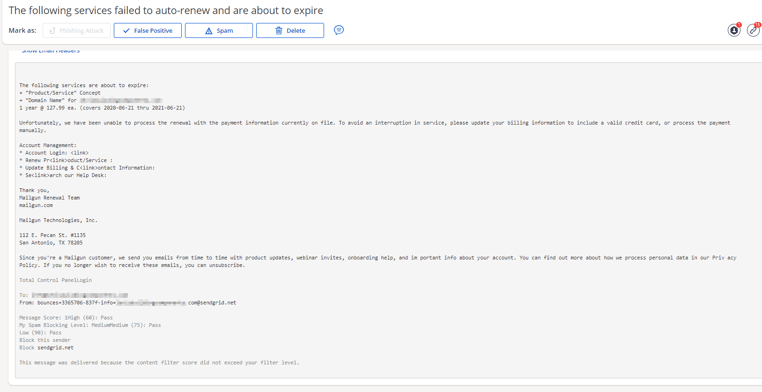
Figures 3 + 4 [SendGrid]

Fake login attacks proliferate as attackers bypass traditional email security tools
Business email compromise (BEC) attacks that deploy social engineering techniques that trick users into taking actions, such as sending a payment or updating a credit card aren’t new. In fact, the FBI estimates over $1.7 billion in losses stemmed from BEC in 2019 alone.
The use of phishing websites with fake login calls-to-action are increasing gaining in popularity due to the ease of deployment and return-on-investment. In fact, the company Bolster reported over 800,000 confirmed phishing websites in just Q1 2020. That’s couple with Verizon’s annual 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, which found that the vast majority of hacking is used for credential theft (~80%) with phishing being the number 1 vehicle to steal those credentials.
As I wrote about earlier this year, fake login phishing websites are especially problematic for companies that rely on rules-based email security such as secure email gateways (SEGs), multi AV scanners and sandboxing solutions, as such tools and solutions lack visual anomaly detection capabilities required to assess a fake login page from a legit login page in real-time.
To help mitigate BEC risks, just last week we announced that we have deployed natural language processing (NLP), using advanced machine learning (ML) and neural networks, to automatically detect and respond to the most common types of business email compromise (BEC) attacks. We’ve also added new capabilities into our platform that will aid in impersonation protections for senior executives. Our press release has all of the details here.
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)












.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)



