Table of Contents
Account Takeover Explained
Account takeover (ATO) is a form of cybercrime that occurs when a cybercriminal gains access to a victim’s online account. The attacker can then use the account to commit fraud, steal money or sensitive data, or commit other malicious activities. ATO is a subset of phishing, and is often used in combination with other advanced phishing techniques, such as business email compromise (BEC).
How does Account Takeover work?
Account takeover attacks can be done in a variety of different ways, including phishing, malware, brute force attacks, and social engineering as some of the most common tactics.
- Phishing: The attacker will attempt to send the victim phishing emails that contain malicious links or attachments. If the victim clicks on the link or opens the attachment, the attacker will be able to install malware on their device, allowing the attacker to gain access to the victim’s online accounts.
- Credential Stuffing: This attack involves using a list of stolen usernames and passwords to gain access to a victim’s account. The attacker will use automated scripts to attempt to log in to the account using the stolen credentials.
- Password Spraying: This attack involves attempting to guess a user’s password by guessing common passwords such as “password” or “123456”. The attacker will use automated scripts to attempt to log in to the account with the guessed passwords.
- Social Engineering: This attack involves tricking the victim into revealing their login credentials. The attacker may do this by posing as a legitimate representative from the service the victim is trying to access, or by creating a fake website that looks like the legitimate one.
Other tactics can include purchasing credentials from the dark web and accessing session cookies or authentication tokens.
Once the attacker has gained access to the account, they can use to commit additional and likely more damaging cyberattacks including:
Financial fraud: using their control of accounts to order goods, use loyalty points, or even send money to themselves.
Data exfiltration: account takeover attacks have the potential to result in the exfiltration of sensitive company data. Consider the fact that employee email inboxes often include sensitive reports, discussions, and spreadsheets.
Malware/ransomware: ATO is a possible path to installing malware or ransomware within a corporate IT environment. An attacker might upload malware with an enticing filename to a shared cloud storage account or launch internal phishing emails leveraging the established trust people between colleagues to spread malicious files through an organization.
To learn more about how ATO works and its different forms check out our blog post.
How to prevent Account Takeover
Strong passwords, two-factor authentication, up-to-date software, security awareness training, and phishing simulation are all essential measures that can help to protect against account takeover (ATO).
Strong Passwords: The use of strong, unique passwords for all online accounts helps to make it difficult for attackers to gain access
Two-factor authentication: adds an extra layer of security, making it even harder for attackers to gain access
Keep software and OS up to date: this helps to ensure that any vulnerabilities are patched, making it harder for attackers to exploit
Security awareness training (SAT): organizations will benefit from running SAT campaigns to help prevent ATO. SAT helps to raise awareness internally of phishing emails and to avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from malicious sources.
Phishing Simulation Testing: phishing simulations can be used to test employees’ knowledge and ability to identify phishing emails. By utilizing all of these measures, organizations can better protect themselves from ATO attacks and reduce the risk of a successful attack.
API security: Securing your API connections is important in the prevention of account takeover (ATO). APIs are used to allow applications to communicate with one another, and if they are not secure, attackers can exploit them to gain access to sensitive data.
Finally, an advanced email security solution capable of protecting against advanced phishing threats like BEC and ATO is critical for all high-value organization targets. These advanced anti-phishing solutions can prevent phishing emails from resulting in access to accounts. Advanced solutions can use machine learning, computer vision, and other technologies to filter out emails containing links to spoofed login pages.
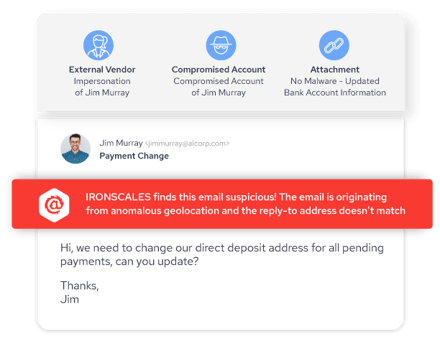
How IRONSCALES ™ uses AI and machine learning technology to protect against ATO
IRONSCALES delivers holistic, comprehensive ATO protection through automated incident response, proactive threat hunting, virtual SOC, personalized security awareness training and real-world phishing simulation testing.
IRONSCALES analyzes content and communication styles in order to detect and prevent even the most sophisticated account takeover attempts. Additionally, IRONSCALES cross checks multiple signals of compromise such as suspicious travel, mail forwarding rules, and BEC language to prevent email account compromise attacks.
Get a demo of IRONSCALES™ today! https://ironscales.com/get-a-demo/
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)