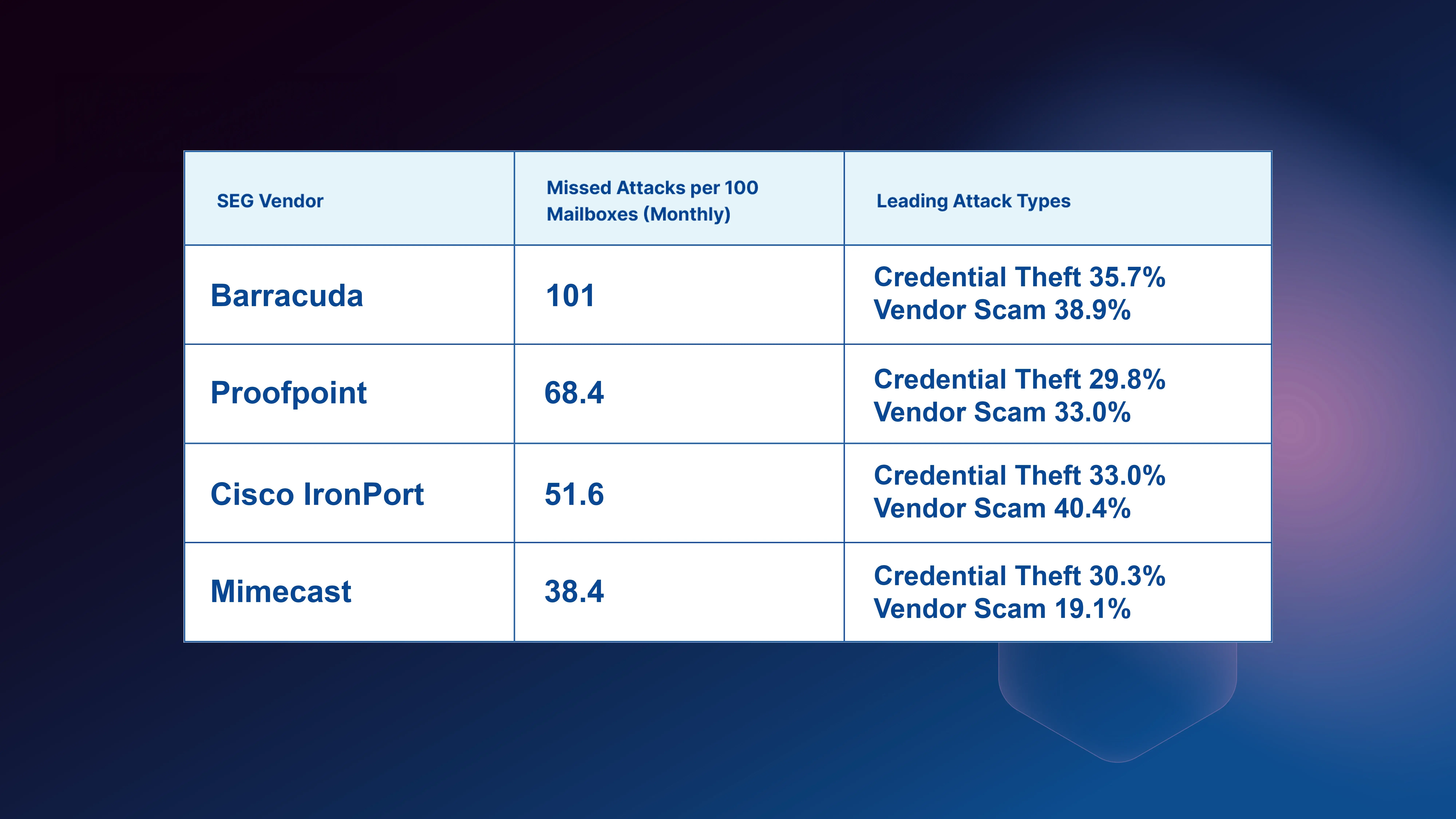
Table of Contents
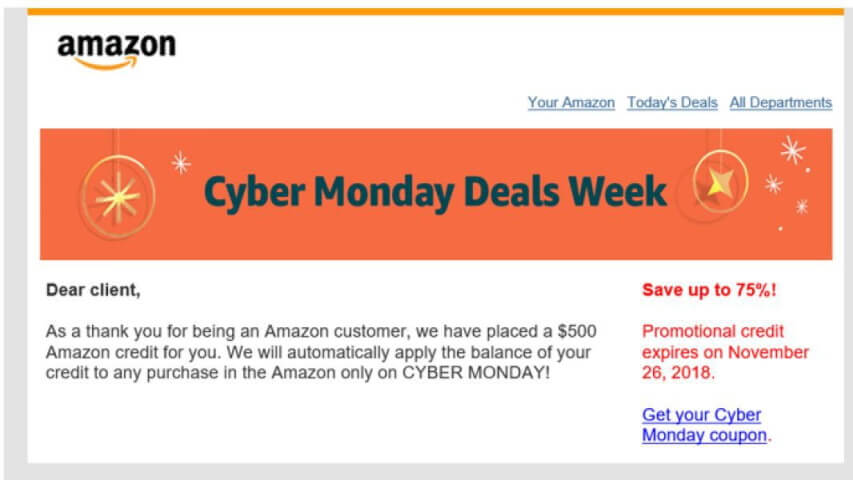
If you follow our blog, then you may have read one of our many articles this year about the growing cyber threat of fake login pages. These nefarious yet often highly realistic-looking pages are now a common tactic deployed by attackers seeking to obtain a person’s login credentials to a legitimate website, such as a bank, email client, or social media site, among many other popular services.
The operation, commonly known as credential theft, is simple: target unsuspecting recipients with an email spoofing a trusted brand and persuade them via social engineering to insert their legitimate credentials, such as a username and password, into a fake login page that is either embedded within the body of the email or built into a phishing website.
Then, once the target enters his or her credentials, attackers have the information they need to log in to a real account and commence with illegal activity, such as credit card fraud, data extraction, wire transfers, identity theft, and more.
Attackers exploit more than 200 brands for credential theft
According to the 2020 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, ~65% of all breaches now result from hacking and/or email phishing attacks. So, to further underscore the severity of today’s hacking and phishing challenges, IRONSCALES researchers spent the first six months of 2020 identifying and analyzing fake login pages, which now are commonly used to support hacks and spear-phishing campaigns.
Here’s a summary of what we found:
- More than 50,000 fake login pages were identified
- More than 200 of the world’s most prominent brands were spoofed with fake login pages
- Nearly 5% (2,500) of the 50,000 fake login pages were polymorphic, with one brand garnering more than 300 permutations
- The most common recipients of fake login page emails work in the financial services, healthcare, and technology industries as well as at government agencies
The top 5 brands with the most fake login pages closely mirror the list of brands that frequently have the most active phishing websites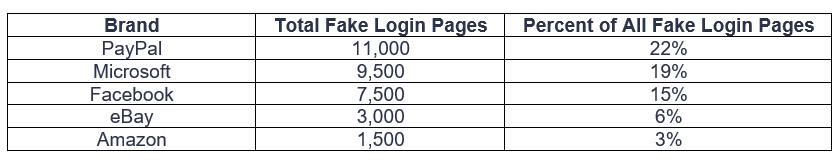
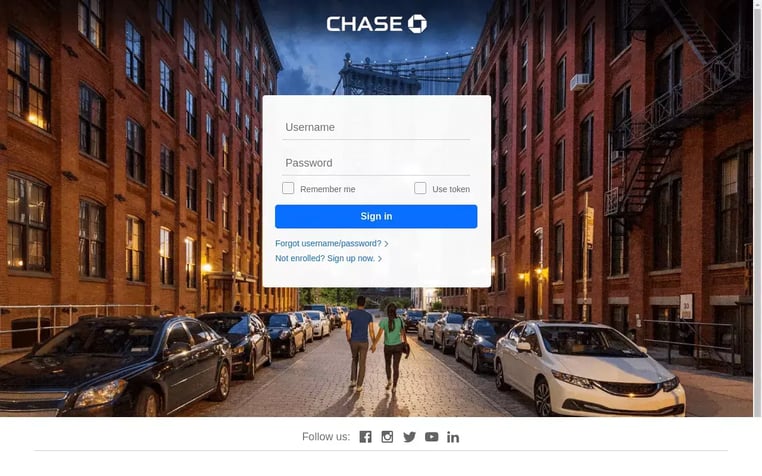
Although PayPal sits atop the list, the greatest risk may derive from the 9,500 Microsoft spoofs, as malicious Office 365, SharePoint and One Drive login pages put not just people but entire businesses a risk.
Additionally, Adobe, Aetna, Alibaba, American Airlines, Apple, AT&T, Bank of America, British Telecom, Delta Air Lines, DocuSign, Coinbase, GoDaddy, Instagram, JP Morgan Chase, Linkedin, Netflix, Stripe, Squarespace, Tesco, Visa, and Wells Fargo were also ranked among the top brands with spoofed login pages 1H 2020.
Download our new eBook with over 100 visuals of active fake login page threats.

Polymorphism rampant with fake logins, leveraging visual impersonations.
Last year we discovered that 42% of all phishing attacks are polymorphic. Polymorphism occurs when an attacker implements slight but significant and often random changes to an emails’ artifacts, such as its content, copy, subject line, sender name, or template in conjunction with or after an initial attack has deployed. This strategic approach enables attackers to quickly develop phishing attacks that trick signature-based email security tools that were not built to recognize such modifications to threats; ultimately allowing different versions of the same attack to land undetected in employee inboxes.
In total, IRONSCALES discovered that nearly 5% of what 50,000 fake login pages identified were polymorphic, with Microsoft and Facebook leading the list with 314 and 160 permutations respectively.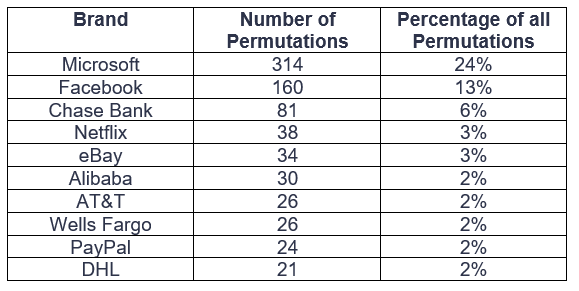
While we cannot say for certain why these brands’ have more permutations than others, we can make an educated guess that this occurred for one of two reasons:
- The security teams associated with these brands are actively looking to take down fake login pages, so attackers are forced to more frequently evolve the attack ever so slightly so to defeat human and technical controls.
- These brands are a priority and or easy target for a certain hacking group(s), so there is more activity and therefore a need to constantly evolve in order to stay one step ahead of security teams.
The success of fake login pages explained
While fake login pages aren’t new, they are increasingly successful for two main reasons.
First, messages containing fake logins can now regularly bypass technical controls, such as secure email gateways and SPAM filters, without much time, money or resources invested by the adversary. This occurs because both the message and the sender are able to pass various authentication protocols and gateway controls that look for malicious payloads or known signatures that are frequently absent from these types of messages.
The second reason can be explained by the psychological phenomenon known as inattentional blindness, which occurs when an individual fails to perceive an unexpected change in plain sight. Inattentional blindness became an internet sensation in 2012 when a video was posted asking viewers how many white-shirted players passed a ball. Intently focused on the task at hand, more than 50% of the viewers failed to recognize a woman in a gorilla suit in the middle of the picture. Even people with phishing awareness training are susceptible to inattentional blindness.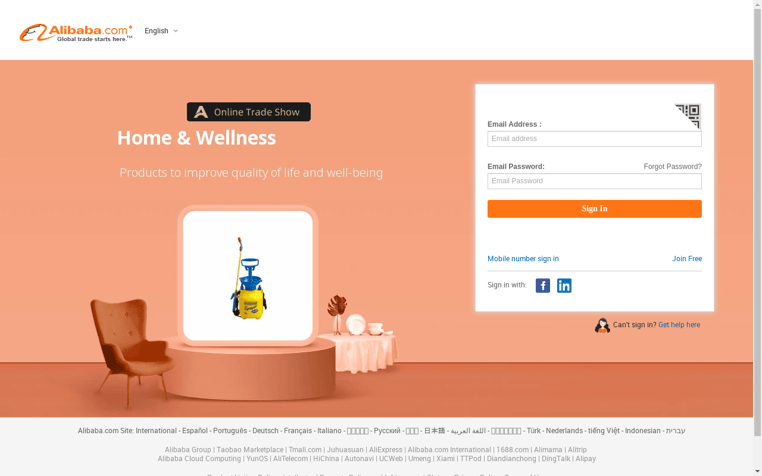
Computer vision and natural language processing needed to identify fake logins
IRONSCALES has the ability to identify fake login pages because of the AI, computer vision, deep learning and natural language processing (NLP) technology built into our self-learning email security platform.
Computer vision and AI play a role in detecting visual anomalies based on learned and trusted profiles (legitimate login pages/websites). While there are some indicators of compromise with fake login pages, such as blurred images, retro branding, and a suspicious sense of urgency, many are unidentifiable using legacy anti-phishing technology or the naked eye.
Further, our NLP uses advanced machine learning (ML) and neural networks to identify the ‘what’ is being sent by analyzing fraudulent language. This allows us to render a verdict on the legitimacy of business email compromise messages, particularly the ones being deployed for credential theft, in real-time.
We invite you to download our new report "The Business Cost of Phishing", where you can discover the true cost of phishing on organizations as well as what IT and Security professionals believe is coming next. You can get the report at https://secure.ironscales.com/the-business-cost-of-phishing/report-download
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)










.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)