Table of Contents
SMTP Explained
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a standard for sending email messages between servers. It was first defined in 1982 and is now the de facto standard for email delivery across the internet. It supports both text and binary attachments, as well as providing authentication and encryption options so that emails can be sent securely. SMTP works by using a client-server model; when you write an email message, your computer contacts the recipient's mail server to deliver it. The mail server then relays the message on to the recipient's computer.
How does SMTP work?
When an email is sent, it first goes to an outgoing mail server using SMTP protocol. This server then checks if the sender has proper credentials and if they do, it scans the address of the intended recipient. If the recipient's address is hosted by another SMTP server, then the message is relayed to that server where it will be either accepted or rejected based on further authentication processes such as SPF records or DKIM signatures. Once accepted, this other SMTP server will store a copy of the message before forwarding it onto its destination.
The Shortcomings of SMTP
Although SMTP is an essential component of most email services today, there are some significant limitations associated with it. For example, authentication techniques used by SMTP are not strong enough to reliably protect against spammers or hackers who might try to gain access to someone else’s account or send malicious messages. Additionally, SMTP does not provide encryption which means that all data transferred between servers is transmitted in clear text instead of encrypted format making it vulnerable to interception or modification by third parties. Additionally, since many ISPs use port 25 for SMTP traffic which can be blocked due to security concerns making it difficult for users to reliably send emails across different networks without facing any issues with their ISP’s policy on port 25 traffic.
There are several foundational security measures that can be taken in order to improve email security beyond what traditional SMTP provides, including:
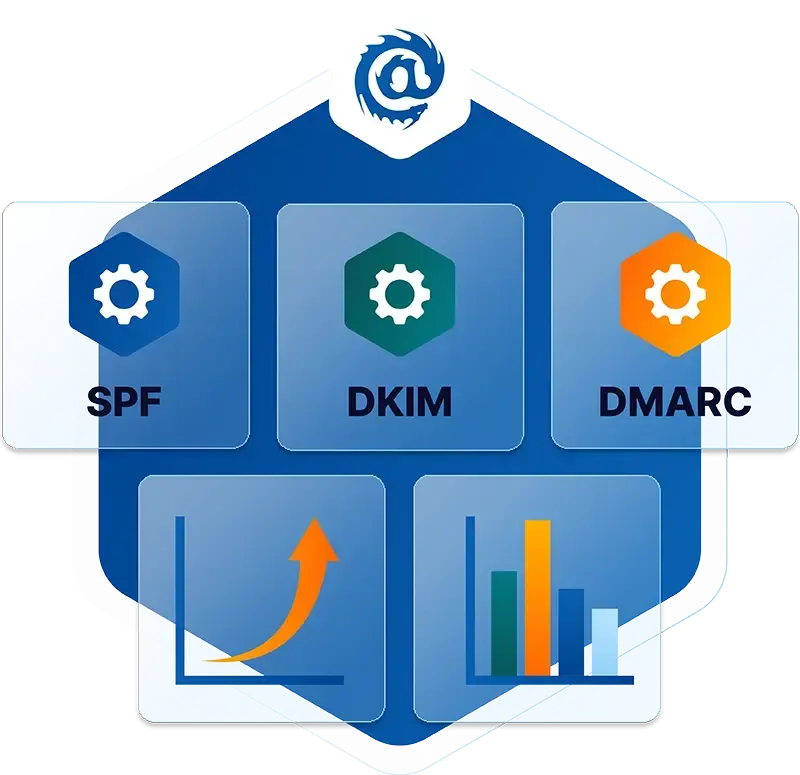
- TLS (Transport Layer Security) encryption which adds an additional layer of protection when sending and receiving data across networks by encrypting data while it is in transit so that only authorized recipients can view its contents.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting & Conformance) which helps verify whether emails sent out from a certain domain were indeed sent by an authorized sender
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework) records which help identify legitimate sources of email within a certain domain
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) which helps prevent spoofed emails from being sent out under false identities
Lastly, implementing an advanced anti-phishing platform to protect against more sophisticated attacks that bypass the security measures including advanced malware, polymorphic attacks, social engineering, and more.
In conclusion, while Simple Mail Transfer Protocol provides adequate functionality when handling email communications over networks, it lacks the necessary security measures to protect against basic and advanced email attacks. For organizations looking to sufficiently protect their email against today's threats they will need expand their security measures and integrate a dedicated email security solution.
Expand email security with IRONSCALES
SMTP, as previously mentioned, has significant gaps in security and implementing additional measures like TLS, DMARC, SPF, and DKIM are a great first step in protecting from malicious actors, however, they do have vulnerabilities that can be exploited.
To further protect your organization and provide truly comprehensive email and messaging security, organizations should consider IRONSCALES™. IRONSCALES is an automated email security solution powered by artificial intelligence and human insights to automatically detect and stop advanced phishing attacks like malware, spoofing, impersonation, business email compromise (BEC), account takeover (ATO) and more. The API-based anti-phishing platform allows for truly comprehensive email and messaging security beyond basic security measures.
Check out the complete IRONSCALES email security solution here.
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)