Table of Contents
In our hyper-connected world, data mishaps are the new normal. Data breaches, data leaks, and data loss have become major concerns for organizations of all sizes. These incidents not only pose significant financial risks but also lead to reputational damage and legal consequences. To safeguard sensitive information and protect their customers' trust, organizations must understand the distinctions between data breaches, data leaks, and data loss. Moreover, implementing robust data loss prevention (DLP) and accidental data exposure (ADE) strategies are crucial for maintaining a secure digital landscape.
Data Breach
A data breach occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive information. Cybercriminals often exploit security vulnerabilities to infiltrate an organization's network or environment, stealing confidential data such as personal identifiable information (PII), financial records, or trade secrets. The motive behind data breaches can range from financial gain through selling stolen data on the dark web, to espionage and sabotage.
Unfortunately, data breaches are common, and their impact on the economy is substantial. The cost of data breaches globally has been rising steadily, highlighting the urgency for organizations to take preventive measures.
Data Leak
A data leak refers to the accidental exposure of sensitive information either at rest or in transit. Data leaks can occur through various avenues, including unprotected databases, misconfigured servers, or human errors like inadvertently sending an email containing confidential data to the wrong recipient.
In some cases, data leaks are the result of cybercriminals obtaining sensitive data through a data breach and then publishing it on the dark web. Data leaks are particularly challenging to detect and remediate promptly, making them a serious threat to organizations' security.
Data Loss
Data loss encompasses incidents where sensitive data is unintentionally misplaced or stolen through cyberattacks or insider threats. While this definition overlaps with data breaches, data loss also includes scenarios where information cannot be retrieved due to human- or system-errors, or hardware failures.
The consequences of data loss can be severe, leading to operational disruptions, financial losses, and damage to an organization's reputation. The downtime cost during a data loss incident can be exorbitant, emphasizing the need for proactive data protection strategies.
Distinguishing Data Breaches, Data Leaks, and Data Loss
While data breaches, data leaks, and data loss share similarities, they are distinct events:
-
-
Data Breach = Access — involves unauthorized access to sensitive information by cybercriminals through security vulnerabilities.
-
Data Leak = Exposure — involves the unintentional exposure of sensitive data, either through human error or overlooked vulnerabilities.
-
Data Loss = Removal — encompasses both accidental and intentional removal of sensitive data, often due to errors or theft.
-
Real-world Data Compromising Events
Data Breach: Equifax
In one of the most significant data breaches in history, Equifax, one of the major credit reporting agencies, experienced a cyberattack in 2017 that exposed the personal information of approximately 147 million individuals. The breach involved sensitive data, including names, Social Security numbers, birth dates, addresses, and in some cases, driver's license numbers. The fallout from this breach was severe, leading to congressional hearings and a settlement of up to $700 million to compensate affected individuals and strengthen data security measures earning it the title of the largest-ever data breach settlement. [1]
Data Leak: Panama Papers
The Panama Papers leak was a massive data exposure that involved 11.5 million documents from the Panamanian law firm Mossack Fonseca. These leaked documents revealed a web of offshore financial dealings and tax evasion by numerous high-profile politicians, celebrities, and wealthy individuals worldwide. The data leak had far-reaching consequences, leading to the resignation of several politicians and triggering investigations and reforms in various countries. [2]
Data Loss: RockYou and RockYou2021
In 2009, RockYou, a social app website, experienced a significant data loss incident when a hacker exploited a SQL injection vulnerability. The breach led to the exposure of over 32 million user passwords stored in plain text. Fast forward to today, and the RockYou list has evolved into the RockYou2021 file with a staggering 8.4 billion entries. Recent studies revealed that just 512,000 of these passwords accounted for nearly all attempted credential-based attacks on two common types of servers over a 12-month period. This incident not only underscores the ongoing risk of using common passwords but also highlights the importance of robust data protection measures, including proper encryption and vulnerability management. [3]
Preventing and Responding to Data Breaches, Data Leaks, and Data Loss
Organizations must adopt proactive measures to prevent these security incidents:
Preventing Data Leaks:
- Outbound Email Protection: An outbound email security solution designed for Accidental Data Exposure (ADE) helps prevent data leaks for an organization by proactively identifying and securing sensitive information before it can be inadvertently exposed.
- Cybersecurity Awareness Training: Educate employees about common cyber threats like phishing and social engineering to reduce the risk of insider-related data leaks.
- Behavioral Analytics: Utilize machine learning-based solutions to identify potential malicious activities and detect insider threats before they escalate.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): Limit access to sensitive information to only those who require it, reducing the chances of unauthorized data exposure. Consider regular audits to ensure compliance and identify vulnerabilities.
Preventing and Responding to Data Breaches:
- Vulnerability Monitoring: Regularly scan and patch vulnerabilities within the organization's network and systems to minimize the risk of breaches.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Implement IDS to monitor network traffic and identify suspicious activities indicative of a potential breach.
- Incident Response Plan (IRP): Develop and practice an effective IRP to swiftly respond to breaches and mitigate their impact.
- Backdoor Detection: Identify and eliminate software backdoors that cybercriminals may exploit to bypass security measures.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies:
- Data Encryption: Employ robust encryption techniques to protect data both at rest and in transit, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Endpoint Security: Strengthen endpoint security with advanced agents capable of detecting and controlling information transfer between users and networks.
- Monitoring Third-party Vendors: Extend data leak detection efforts to include monitoring third-party vendors' data leaks to ensure data security across the supply chain.
Conclusion
Data breaches, data leaks, and data loss are significant cybersecurity challenges that organizations must address comprehensively. By understanding the differences between these incidents and implementing robust prevention strategies, businesses can protect their sensitive data and maintain the trust of their customers. Proactive data loss prevention measures, combined with a strong incident response plan, are critical components of a comprehensive cybersecurity approach that helps safeguard against these evolving threats.
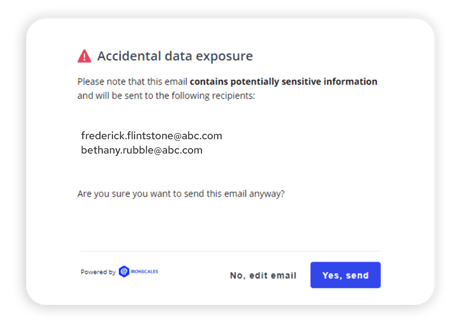
IRONSCALES Introduces Accidental Data Exposure Prevention Capabilities
IRONSCALES help prevent email-driven accidental data loss with real-time alerts. These mailbox-level alerts increase employee awareness and safeguard against the inadvertent transfer of sensitive data. The IRONSCALES Accidental Data Exposure capability utilizes advanced technologies to promptly identify and notify employees about emails that may leak sensitive data—enhancing their security awareness and proactively preventing potential data leaks in real-time.
References:
- Equifax Data Breach: "Equifax to Pay at Least $650 Million in Largest-Ever Data Breach Settlement" (NYT)
- Panama Papers: "THE PANAMA PAPERS: EXPOSING THE ROGUE OFFSHORE FINANCE INDUSTRY" (ICIJ.org)
- Dark Reading: "List of Common Passwords Accounts for Nearly All Cyberattacks" (DarkReading.com)
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)









.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)





