Table of Contents
Introduction
The release of the 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) offers valuable insights into the current state of cyberthreats and data breaches. In this comprehensive analysis, we will delve into three key focal points report including Vulnerabilities, Threats, and Targets. By examining these areas in depth and extracting insights and key takeaways from the report, we aim to provide organizations with a thorough understanding of email security and evolving cyberthreats, along with effective strategies to mitigate risks.
Vulnerabilities: Humans, Rarely System Exploits
Human Error
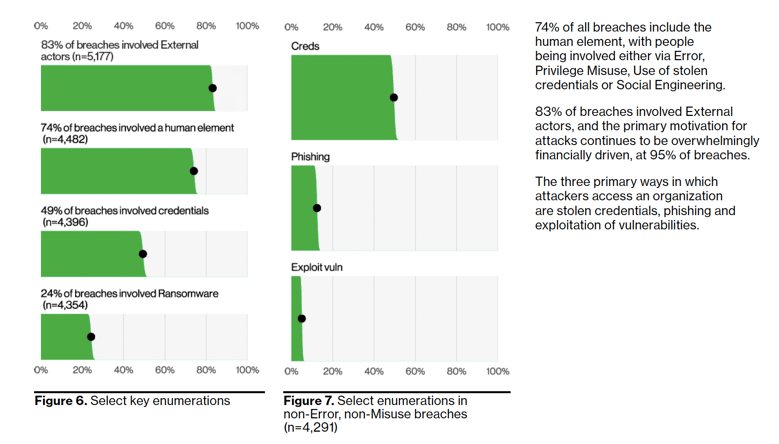
Human error, privilege misuse, stolen credentials, and social engineering are all factors that contribute to 74% of data breaches. Attackers take advantage of human vulnerabilities to manipulate individuals into sharing sensitive information or engaging in actions that can result in breaches. The 2023 DBIR reports that social engineering incidents, particularly phishing-based attacks, make up 44% of these breaches, while pre-texting (Business Email Compromise) incidents are also on the rise.
Knowing that humans are the leading cause of breaches within organizations developing a human-centric security strategy that puts employees at the core your approach is critical in being successful with preventing breaches. An organizations approach to cybersecurity must prioritize the understanding and integration of human behavior and enablement within the context of security measures. It recognizes that humans play a critical role in an organization's security posture and aims to develop strategies and practices that align with human needs, motivations, and capabilities.
This human-centric security manifests itself later in this blog in response to combatting social engineering based attacks like, business email compromise (BEC), and implementing a comprehensive security awareness training and phishing simulation program that both educates end users and enables them to serve as an extension of an organizations defense by reporting advanced threats like BEC.
System Exploits: Log4j and CVE-2021-44228
While data breaches involving system exploits share less than 5% of total data breaches, one common culprit consistently emerged: Log4j. Verizon's data contributors' revealed that Log4j was chief among their grievances, with 90% of incidents involving an exploit vulnerability mentioning "Log4j" or "CVE-2021-44228" in the comments section. Surprisingly, only 20.6% of their reported incidents had comments, highlighting the significance of Log4j in the realm of system exploits.
 Source: 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report
Source: 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report
Threats: System Intrusion
Ransomware: We're still talking about this?
Despite it being an on going issue for decades ransomware remains to be a leading danger for organizations across various sectors and sizes, accounting for 24% of breaches. Within these cases, an alarming 94% fall under the category of System Intrusion. Although there has been a slight increase in Ransomware attacks this year, their prevalence is so widespread that it has become a persistent threat that we must constantly guard against. In fact, a staggering 91% of industries consider Ransomware as one of their top three security concerns.
To gain insights into how these attacks take place, it is valuable to explore the primary vectors utilized by cybercriminals. In this context, the most common entry points are Email Desktop sharing software, and Web applications. Email as a vector shows no signs of fading away anytime soon. Its convenience, allowing for the delivery of malware and enticing users to execute it, has rendered this technique timeless. The prominence of Desktop sharing software as a vector is understandable, as breaches often involve gaining access to a system. What better way to achieve this than leveraging built-in tools like RDP or third-party versions, providing cybercriminals with an intuitive graphical interface?
System Intrusion incidents continue to pose a significant threat, often involving ransomware attacks, vulnerability exploits, and the use of stolen credentials. Attackers constantly adapt their techniques to evade security controls and achieve their objectives.
Social Engineering: Business Email Compromise (BEC), Pre-texting, and Credential Harvesting
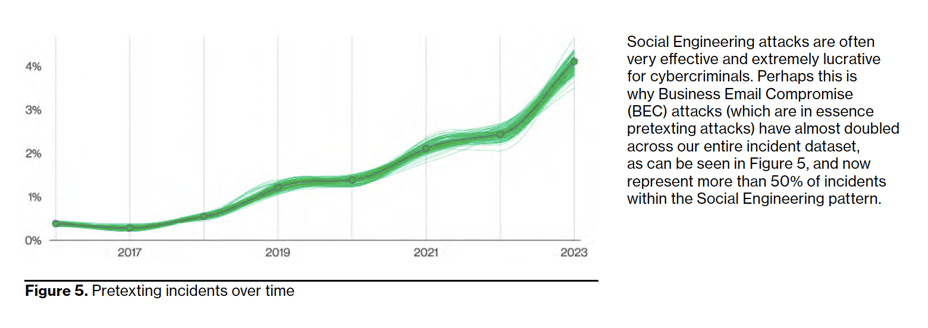
Social Engineering attacks continue to be highly effective and profitable for cybercriminals, which is why Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks, a form of pretexting, have nearly doubled in Verizon's 2023 incident dataset and now account for over 50% of Social Engineering incidents.
Similar to the deceptive nature of Ransomware, which seeks to profit from unauthorized access to an organization's network, Business Email Compromise (BEC) is another method employed by criminals to exploit access to a user's inbox and contacts. BEC attacks can be targeted internally, where attackers impersonate a trusted source or exploit a compromised employee's email account to deceive their own organization. A common tactic involves redirecting payroll deposits into the attacker's account, allowing them to seize control of financial transactions. Alternatively, actors can target partners, agencies, and customers by using access to an employee’s email account, so they can impersonate that user and request updates to payments in order to include their own bank account.
Credential harvesting and its continued rise has become a significant concern in cybersecurity. As evidenced by the 2023 Verizon DBIR, out of the 1,404 reported incidents, a staggering 1,315 resulted in successful data breaches due to compromised credentials. That is data breach rate of 93.6% indicating a significantly higher success rate compared to traditional incident types. This highlights the alarming effectiveness of credential harvesting techniques employed by attackers, emphasizing the urgent need for robust security measures like multi-factor authentication to mitigate the risk.
 Source: 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report
Source: 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report
IRONSCALES Recommendations
To effectively mitigate the risks associated with system exploits or social engineering, IRONSCALES recommends organizations should prioritize the following strategies:
-
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Using MFA is crucial for protecting against credential harvesting because it adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification beyond just their passwords, making it significantly more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts even if passwords are compromised.
- Patch and Vulnerability Management: Regularly apply security patches and updates to eliminate known vulnerabilities in software, operating systems, and applications. Organizations must prioritize patch management to address critical vulnerabilities promptly.
- Advanced Email Security: An advanced email security platform is a crucial component of any organization's cybersecurity strategy. With the increasing sophistication of email threats like BEC organizations need AI-powered solutions that can identify and block these threats in real-time.
- Security Awareness and Training: Implement a comprehensive security awareness training program that educates employees about social engineering techniques, the importance of email security, and how to identify and report suspicious activities. Regular training and personalized phishing simulations can significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to BEC attacks. In addition to, establishing clear and easily accessible methods for employees to report suspicious emails or activities promptly.
- Access Control Management: Employ robust access control measures to manage user, administrator, and service account credentials. This includes implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and regularly reviewing and revoking access privileges. By limiting unauthorized access, organizations can mitigate the risk of BEC attacks and unauthorized data exposure.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Using MFA is crucial for protecting against credential harvesting because it adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification beyond just their passwords, making it significantly more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access to accounts even if passwords are compromised.
Targets
In this section, we will pulled out two specific target groups from the 2023 DBIR, focusing on Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs) and the North America region. Findings from the report shed light on the prevalent risks faced by SMBs, emphasizing the need for tailored cybersecurity strategies to mitigate these evolving threats effectively. Furthermore, we will examine the rising percentage of threat actors and data compromises originating from within organizations in North America.
Organization Size: Small and Medium Businesses (SMB)
As both small and large companies increasingly rely on similar services and infrastructure, their vulnerabilities to cyberattacks have become more similar as well. This convergence of attack profiles disregards the size of the organization. However, the ability of organizations to respond to these threats differs significantly based on the resources they can allocate in the event of an attack. The 2023 DBIR highlights the increasing targeting of Small and Medium Businesses (SMBs) by cybercriminals. SMBs are often seen as attractive targets due to their potentially weaker security controls and limited resources for cybersecurity.
Region: North America
The North America region continues to have to prepare itself for the bleeding-edge of cyberattack strategy and technology. North American organizations are experience a concerning trend, with cyberattacks and data compromises increasingly originating from internal sources within organizations. According to the DBIR, North America ranked the highest for its share of threat actors and data breaches resulting from internal sources including compromised accounts and impersonation incidents. North America has 6X more of its threat actors internally than that of EMEA, 2.4X than LAC, and 1.3X more than APAC.
IRONSCALES Recommendations
To enhance cybersecurity defenses and protect against evolving threats, IRONSCALES recommends SMBs should focus on the following strategies:
-
-
Risk Assessment and Prioritization: Conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and prioritize security investments based on their potential impact. This enables SMBs to allocate limited resources effectively and implement targeted security controls
-
Advanced Threat Protection: SMBs should strongly evaluate implementing an AI-powered email security solution for automated advanced threat protection (ATP) including real-time behavior analysis. Email is still the leading source for data breaches making advanced critical for SMBs to effectively safeguard themselves against advanced cyberthreats, especially when operating with limited resources.
-
Managed Security Services: Consider partnering with managed security service providers (MSSPs) to outsource security monitoring, threat intelligence, and incident response capabilities. MSSPs can offer expertise and cost-effective solutions tailored to the needs of SMBs.
-
Incident Response Planning: Develop an incident response plan specifically tailored to the needs and resources of SMBs. The plan should outline clear response procedures, communication protocols, and collaboration with external parties such as law enforcement or incident response experts.
-
Conclusion
The 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report serves as a valuable resource for organizations seeking to enhance their email security and defend against evolving cyberthreats. By focusing on mitigating vulnerabilities associated to the human element via training and end-user enablement organizations can significantly reduce the risks of a data breach. Additionally, implementing effective strategies for System Intrusion defense, such as patch management, MFA, and AI-powered email security solutions, strengthens overall security posture.
Leveraging the insights and recommendations from the DBIR, organizations can fortify their defenses, safeguard critical assets, and stay ahead of emerging cyberthreats.
Get the full 2023 Verizon DBIR report here.
View our On-Demand Webinar "Decoding the 2023 Verizon DBIR: Unveiling Key Insights and Actionable Takeaways" here.
Explore More Articles
Say goodbye to Phishing, BEC, and QR code attacks. Our Adaptive AI automatically learns and evolves to keep your employees safe from email attacks.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)















.webp?width=100&height=100&name=PXL_20220517_081122781%20(1).webp)