Guide to preventing domain spoofing
Domain spoofing occurs when an attacker impersonates a trusted domain name during a phishing attack. For example, an attacker may send an email from a domain that appears to be legitimate. Alternatively, they may set up a scam page that imitates a legitimate site and uses a nearly identical domain name, tricking you into entering login credentials, credit card information, or other sensitive data.
This article explores how domain spoofing attacks work and the top mitigation and prevention strategies you can use to avoid falling victim to domain spoofing attacks.
Summary of key domain spoofing defenses
For reference, let’s briefly overview how organizations can combat domain spoofing. Later in the article, we’ll explore these defense tactics in greater depth.
| Defense |
Explanation |
|
Email Protocols
|
DMARC and related email security protocols make it harder for attackers to impersonate your domain when sending spam and phishing emails.
|
| Email security solutions |
Tools like SEGs and ICES scan incoming and outgoing mail for signs of threats and perform many more crucial functions to protect you. |
| Security Awareness Training |
SAT trains employees not only to avoid falling victim to phishing but also to identify and report threats proactively. |
| Phishing simulation campaigns |
Phishing simulations allow you to discover which parts of your organization are most vulnerable to phishing threats. |
How domain spoofing works
Let’s suppose your company sends invoices to customers. An attacker wants to trick your customers into paying an invoice to them instead of to your business! So to aid with this, they decide to impersonate your domain. Note, if you don’t have DMARC set up, they can just send unauthorized emails directly from your domain! However, even with DMARC, they can purchase a domain that looks visually similar to yours.
Once the attackers have purchased a visually similar domain, they will then set up a fake webpage that looks exactly like one of your log in pages; they may even add add SPF and DKIM authentication (more about that later). Victims of their phishing emails might go to this site and enter sensitive financial data or credentials, especially if the email looks similar to notifications they get on a regular basis, such as notifications of updates posted to a secure portal, frequently used in medical, legal, and real estate industries. For example, they may use the website to have customers pay fake invoices. This data will then be sent over to a server controlled by the attackers.
Case study: Walmart typosquatting attack
Several years ago, attackers used domain spoofing to launch a spam campaign targeting Walmart customers. However, if you look up Walmart’s DNS records, they have a strong DMARC policy to protect against domain spoofing.
$ dig txt _dmarc.walmart.com
...
_dmarc-r.walmart.com. 7200 IN TXT "v=DMARC1; p=reject; fo=1;
...
To counter this, the scammers resorted to typosquatting. They purchased a domain name similar to walmart.com but used the capital “L” instead of the lowercase “l” in the word Walmart. Since waLmart.com and walmart.com are visually identical, email recipients often missed the difference. The attackers were even able to set up DMARC for the typosquatting domain, adding to its apparent legitimacy!

Domain spoofing prevention and best practices
Conceptually understanding domain spoofing is helpful, but essential knowledge for security engineers is how to defend their organizations from this kind of attack. Although DMARC cannot protect against typosquatting, modern AI/ML-driven solutions are capable of noticing and flagging blatant typosquats. This section reviews solutions and best practices that help mitigate and prevent domain spoofing.
Email security protocols
The email security ecosystem is a mature, well-developed space with many technology solutions available. This includes solutions that use widely adopted email protocols that have developed over the years to attempt to make email more secure. Two necessary email protocols are given below.
Other, more niche email security protocols are also worth knowing. One example is BIMI. According to the IRONSCALES glossary entry on BIMI:
“As the newest and least utilized email authentication standard, BIMI intends to reduce fraudulent brand spoofing emails by visualizing a logo as a measure of authenticity. Compliance requires DMARC configuration with active “quarantine” or “reject” policies, a positive sender reputation, and a BIMI Assertion Record.”

Email security solutions
You should use email security solutions for two reasons:
- Prevent and block emails from someone impersonating your domain and targeting your employees.
- Prevent and block emails spoofing third-party businesses but attempting to steal confidential data from your employees.
A Secure Email Gateway (SEG) sits upstream from your email server or cloud hosted service and filters incoming and outgoing email. SEGs address malicious spam and basic phishing emails–some also provide email encryption, archiving, and data loss prevention. Unfortunately, IRONSCALES research shows that advanced phishing attacks bypass SEG defenses at an alarmingly high rate. The graph below shows how many emulated phishing emails led to successful penetrations against various SEG providers.
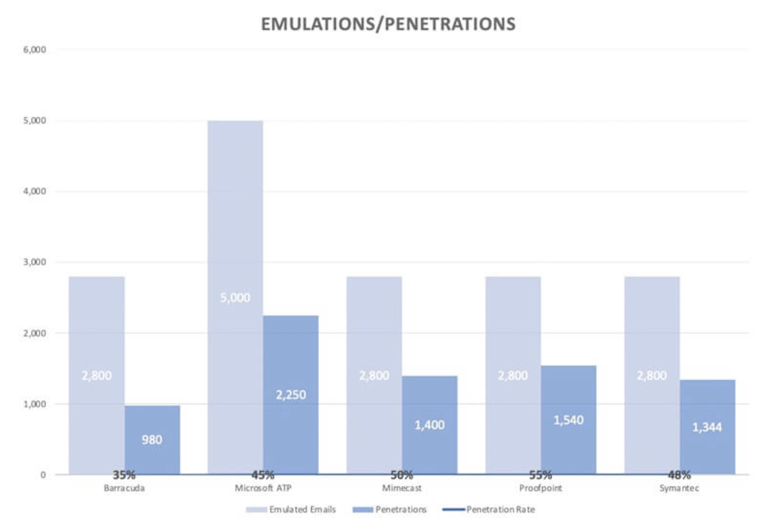
Advanced phishing attacks often lead to successful penetrations, even when SEGs are used (source).
Newer Integrated Cloud Email Security (ICES) solutions have emerged that address the shortcomings of traditional SEGs. These solutions integrate directly into the cloud email platform via APIs rather than acting purely as an external gateway, similar to a traditional firewall. The tight integration of ICES allows them to go beyond the filtering capabilities of a SEG. Instead, they use AI and machine learning to automatically learn employee email behavioral patterns to enable AI/ML models to detect abnormal emails and emails with malicious intent.
Security Awareness Training
Employee security awareness training (SAT) extends beyond mere instructions on following fundamental security guidelines. SAT involves educating employees on complex threats like:
- Identifying domain spoofed emails
- Business email compromise (BEC) assaults
- VIP impersonations - fake emails pretending to be from top management
Employees who receive comprehensive training are less susceptible to falling victim to phishing attacks. Additionally, SAT enhances the collective intelligence of the workforce, as employees who possess security awareness are better equipped to identify potential threats. Therefore, you should regularly administer SAT and assess employee engagement with the material to ensure understanding.
Phishing Simulation Campaigns
By simulating an actual email attack, you can learn which parts of your organization are most vulnerable to phishing and implement additional training accordingly. Long gone are the days when running an internal phishing simulation campaign required hiring expensive external auditors or having to manually create your own simulation (after creating a fake domain and adding that to the allow list of your SEG). Now there are cutting-edge email security solutions that offer integrated phishing simulation functionality. For example, IRONSCALES includes phishing simulation training that can automatically determine who needs to be tested and recommend campaigns that use content based on attacks they will see in their world. In addition, you can pair the simulations with SAT material geared toward the priorities of your threat model.

Conclusion
Domain spoofing involves impersonating a legitimate, trusted domain. This can occur when attackers send an email appearing to originate from a domain they don’t really control or when attackers trick you into browsing to a site whose domain impersonates the one you trust.
Defending against domain spoofing is possible using layers of security countermeasures. Primary defenses like deploying email protocols like DMARC go a long way. Still, more sophisticated technologies like ICES are worth investing in for organizations that want to improve their overall security posture.

/Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp?width=568&height=326&name=Concentrix%20Case%20Study.webp)










